ParaView/Users Guide/Calculator
Basics
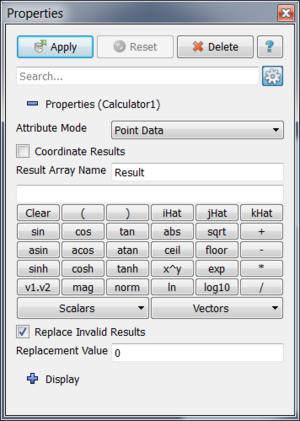
The Calculator Filter can be use to calculate derived quantities from existing attributes. The main parameter of the Calculator is an expression that describes how to calculate the derived quantity. You can enter this expression as free-form text or using some of the shortcuts (buttons and menus provided). Here we describe various options available within the Calculator.
Note: We recommend that you use the Python Calculator instead of Calculator if possible. The Python Calculator is more flexible, has more functions and is more efficient. However, it requires that ParaView is compiled with Python support and that NumPy is installed.
Let's start with a simple example. Create a Wavelet source and then apply the Calculator using "1" as the expression. Note: You can enter an expression by clicking in the expression entry box and typing. This should create an point array called "Result" in the output. A few things to note:
- The Calculator copies the input mesh to the output. It is possible to have the calculator to change the point coordinates. We will discuss this later.
- The expression is calculated for each element in the output point or cell data (depending on the Attribute Mode).
Next, change the expression to be "5 * RTData" and the Result Array Name to be "5 times rtdata" (without the quotes). If you change to surface representation and color by the new array, you will notice that the filter calculated "5 * RTData" at each point.
The main use case for the Calculator is to utilize one or more input arrays to calculate derived quantities. The Calculator can either work on point centered attributes or cell centered attributes (but not both). In order to help enter the names of the input arrays, the Calculator provides two menus accessible through the "Scalars" and "Vectors" buttons. If you select an array name from either menus, it will be inserted to the expression entry box at the cursor location. You can also use the other buttons to enter any of the functions available to the Calculator. Most of these functions are obvious. We will cover the ones that are not below.